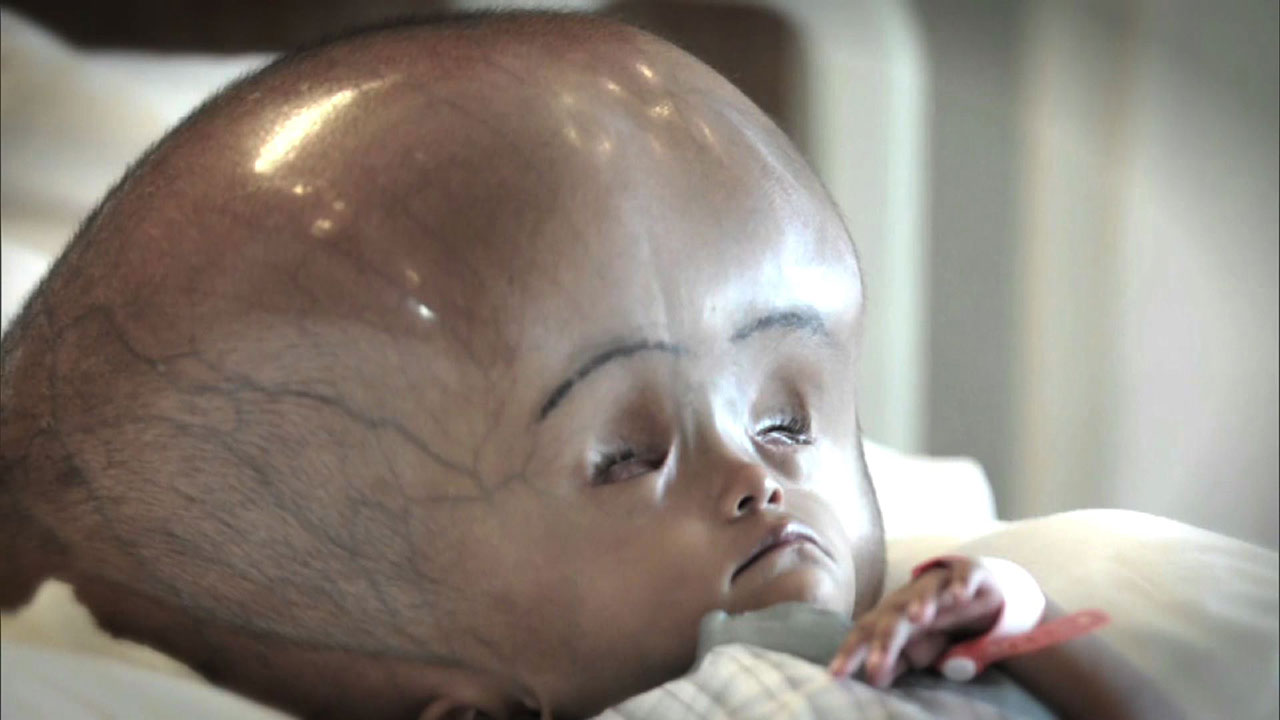
Hydrocephalus (from Greek hydro-, meaning "water", and kephalos, meaning "head") is a condition characterised by abnormal accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) in the brain which causes increased intracranial pressure. This may cause progressive enlargement of the head if it occurs in childhood, potentially causing convulsion, tunnel vision, seizures and mental disability.
Causes include genetic problems and problems with foetal development. An unusually large head is the main sign of congenital hydrocephalus.
Hydrocephalus can also happen after birth. This is called acquired hydrocephalus. It can occur at any age. Causes include head injuries, strokes, infections, tumors, and bleeding in the brain.
Hydrocephalus can cause permanent damage of brain tissue, causing problems with physical and mental development. Left untreated, it is usually fatal. Treatment usually involves surgery to insert a shunt to drain the CSF into other parts of the body where it is absorbed. Medicine and rehabilitation therapy can also help. |
Comments
There are no comments yet!